Introduction to Spark 3.0 - Part 9 : Join Hints in Spark SQL
Spark 3.0 is the next major release of Apache Spark. This release brings major changes to abstractions, API’s and libraries of the platform. This release sets the tone for next year’s direction of the framework. So understanding these few features is critical to understand for the ones who want to make use all the advances in this new release. So in this series of blog posts, I will be discussing about different improvements landing in Spark 3.0.
This is the ninth post in the series where I am going to talk about join hints. You can access all posts in this series here.
TL;DR All code examples are available on github.
Join Hints
In spark SQL, developer can give additional information to query optimiser to optimise the join in certain way. Using this mechanism, developer can override the default optimisation done by the spark catalyst. These are known as join hints.
BroadCast Join Hint in Spark 2.x
In spark 2.x, only broadcast hint was supported in SQL joins. This forces spark SQL to use broadcast join even if the table size is bigger than broadcast threshold. The below code shows an example of the same.
val salesDf = sparkSession.read.
format("csv")
.option("header", "true")
.option("inferSchema", "true")
.load("src/main/resources/sales.csv")
val customerDf = sparkSession.read.
format("csv")
.option("header", "true")
.option("inferSchema", "true")
.load("src/main/resources/customers.csv")
//broadcast hint
val broadcastJoin = salesDf.hint("broadcast").join(customerDf,"customerId")
broadcastJoin.show()In above code, we are specifying the broadcast join using the hint function. We can observe the same join on spark UI.
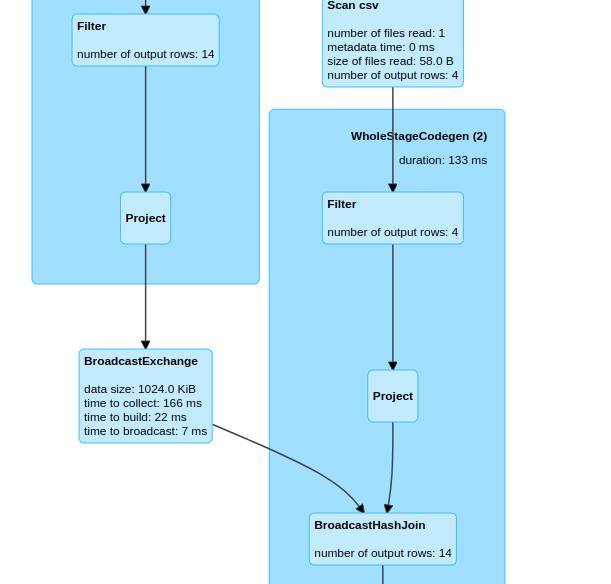 .
.
Extending Hint Framework for Other Joins in Spark 3.0
In spark 2.x, only broadcast join hint was supported. In Spark 3.0, this framework is extended for the other joins also. This allows developers to specify more kinds of joins using this framework.
In rest of the post, we will see how to use other hints.
SortMerge Join Hint
SortMerge join is a most scalable join in spark. We can force it by using merge hint.
val mergeJoin = salesDf.hint("merge").join(customerDf, "customerId")The same can be observed in spark UI also.
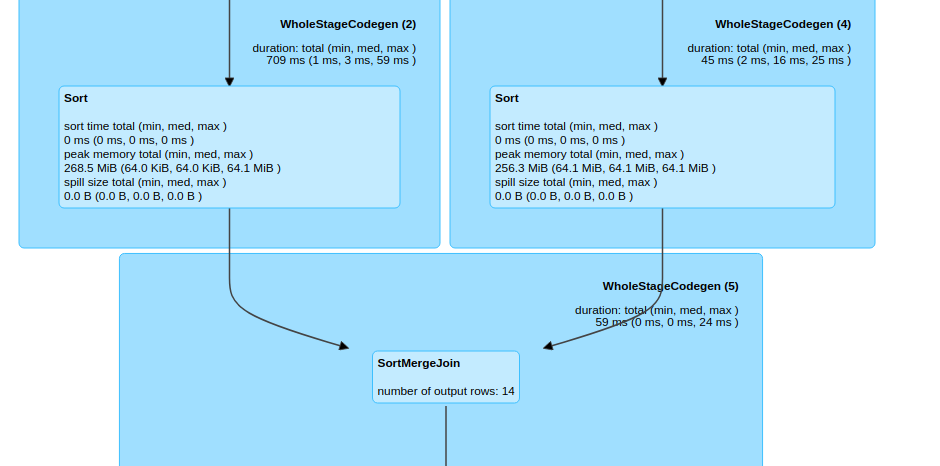 .
.
Shuffle Hash Join Hint
Shuffle Hash Join is a join where both dataframe are partitioned using same partitioner. Here join keys will fall in the same partitions.
This join can be forced using shuffle_hash hint.
val shuffleHashJoin = salesDf.hint("shuffle_hash").join(customerDf,"customerId")The same can be observed in spark UI also.
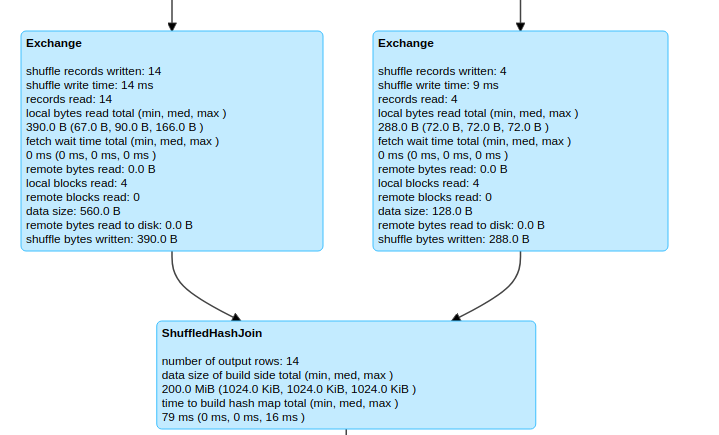 .
.
Cartesian Product Hint
Cartesian Product is one type of join where two dataframe are joined using all rows.
This join can be forced using shuffle_replicate_nl hint.
val cartesianProduct = salesDf.hint("shuffle_replicate_nl").join(customerDf)The same can be observed in spark UI also.
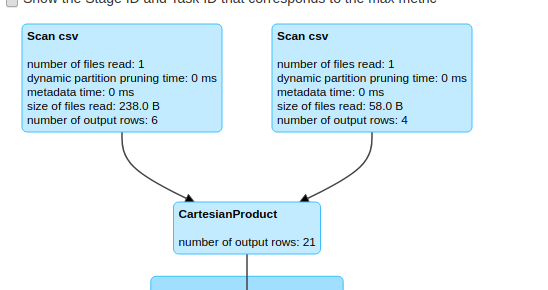 .
.
Code
You can access complete code on github.
References
https://issues.apache.org/jira/browse/SPARK-27225.
Conclusion
Join hints are powerful way for developer to optimise their joins. Spark 3.0 brings all the possible joins to spark SQL hint framework.