Building Read it later service on MEAN stack - Part 1
Recently I gave a talk on how to build RESTful services on MEAN stack. As part of the talk, I went through a step by step tutorial to build read it later service on top of the MEAN stack.
With interest shown by audience, I thought it is good to document the tutorial so that it will be available for any one who dint attend the talk. So in next series of posts, I will be discussing what is MEAN stack and how you can build a read it later service from scratch on MEAN stack.
This is the first post in multi-post series , where I will be discussing about what is MEAN stack and what is it good for.
tl;dr You can grab slides from slideshare and code from github.
What is a software stack?
Software stack is set of tools working together to solve a specific problem. Typically these tools are created and can be used independently. But when these tools are put together as a stack,they give better results.
One of the example of software stack is LAMP stack.It contains Linux, Apache web server, Mysql and PHP. As you can see, all of these technologies are created independently and can be used separately. But if you put them together as LAMP stack, you get a powerful toolbox to create great websites.
What is MEAN stack?
MEAN stands for Mongodb, Express, Angular and Node. It’s a JavaScript based software stack to build web applications.
Why MEAN stack?
You may have heard about LAMP stack before. LAMP stack was created for building powerful websites. But it was 1990’s. Times have changed. Now we are building more and more web applications rather than building websites. So we need a better stack which can support rapid development of web applications. MEAN stack helps you to build the web applications rapidly compare to LAMP stack.
MEAN vs LAMP
| LAMP | MEAN |
|---|---|
| Linux | V8 |
| Apache | Node.js |
| Mysql | Mongodb |
| Php | Express |
The above table shows the difference between LAMP and MEAN. I am cheating little bit here. V8, the JavaScript runtime of Chrome, is not a operating system. It’s a virtual machine which is available on all the operating system. But with trend of virtual machines like JVM,CLR the dependence on operating system is fading. So MEAN stack can run any platform.
We use mongodb in place of Mysql for storage. We use express in place of Php for MVC. Node.js will replace apache for web server.
You may be wondering where is angular. There is no equivalent in LAMP for angular. So it is not shown in the table.
Why to move from LAMP to MEAN
LAMP was created to build websites. It’s not suitable for building web applications, where we will be predominately building REST based API’s. There is a lot of overheads to create the REST services on LAMP. But with MEAN you can build those with very less effort.
In next section, we are going to look at how it looks to create REST web applications in LAMP vs REST on MEAN stack.
REST in LAMP
The following picture shows what it takes to build a REST service in LAMP
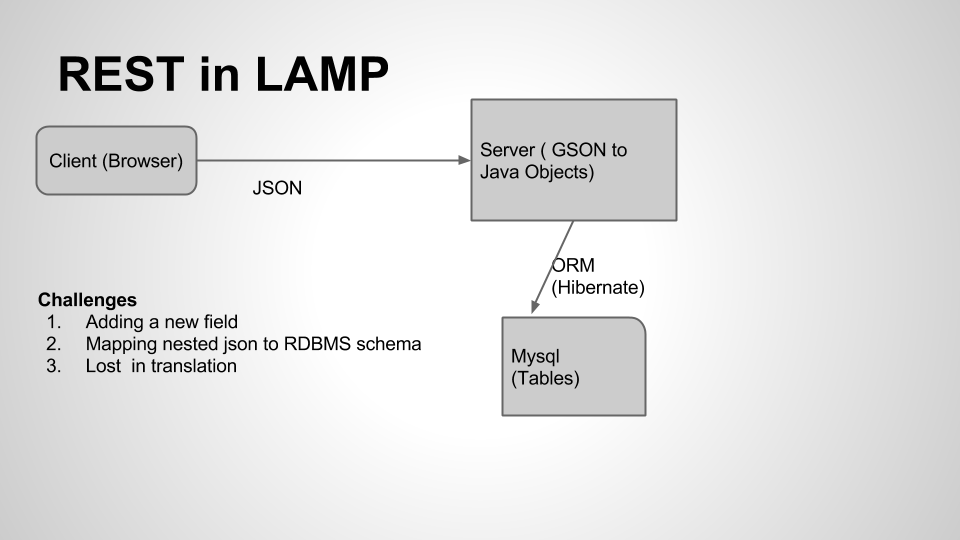
The following are the over heads
Adding a new field
If you want to add a new field, you have to change in lot of places. First you have to change in client side json, then in the server side Java model, then in ORM mapping and finally in the database table. These kind of over head adds strain on rapid development.
Mapping nested json to RDBMS
Typically json has great support for nested structures. But expressing the nested structures in RDBMS is hard.
Lost in translation
It’s very easy to forget update model in one of the places mentioned above and loose the data.
REST in MEAN
Now let’s see how a REST application looks in MEAN stack
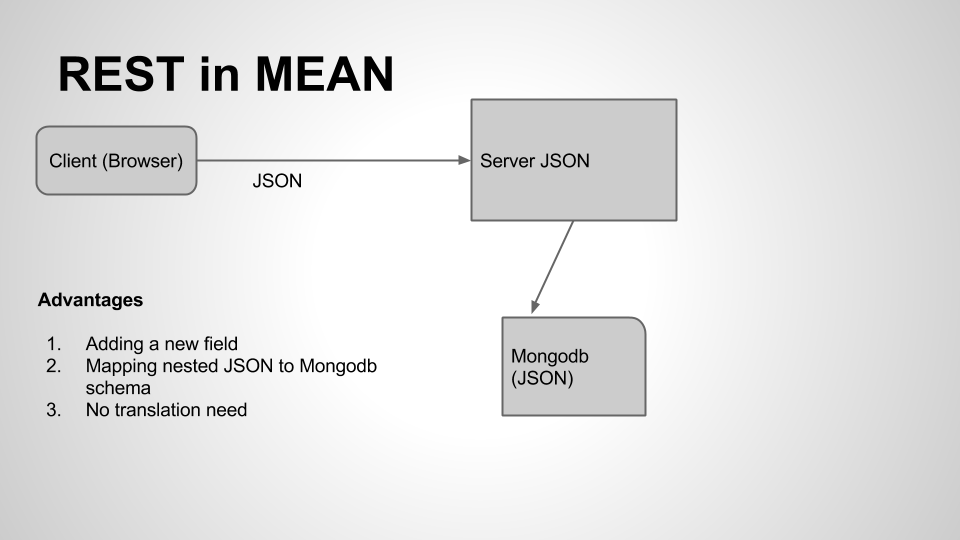
As you can see in the above picture, there is almost no translation. It’s easy to add new field in one place and have it update in all places simultaneously.Yes even database can store data json with Mongodb!!.
JSON is the secret sauce of MEAN stack
JSON stands for JavaScript Object Notation. It’s a data format like XML. It’s the JSON which makes MEAN work like magic. All components in MEAN talk JSON natively. This means there is no time wasted translating from one language to another language.
What MEAN is good for?
Now you understand, building REST applications are much easier in MEAN stack. Now you may be wondering what else REST can do?. The following are few places you can use MEAN
- CRUD web applications
- REST API servers
- Single page apps
- Static content servers
Anything I/O bound is good for MEAN
What MEAN is not good for?
MEAN is not good for all the applications. The following are few of the examples
- Computation intensive applications
- Number crunching systems
- Transactional systems.
In the next post, we will be discussing more about individual pieces of MEAN stack.